Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 6 No. 2 1994 Dec, p. 102-108
COMMON/SPEAR ROT CROWN DISEASE IN OIL PALM (ELAEIS GUINEENSIS JACQ.) : ANATOMY OF THE AFFECTED TISSUE
Received: 17 November 1993 Accepted: 21 March 1994
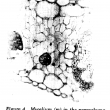
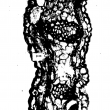
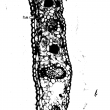
Bent rachises in palms with symptoms of “crown disease” had fibres with thinner and less lignified cell walls than normal cells. Also, vascular bundles were less numerous, thinner, and had fewer fibres than healthy tissue. The first symptom observed before necrosis in leaflets was the collapse of the hypodermal cells. Fungal mycelium was found intercellularly in some preparations. The structural changes observed explain, in part, the softness of these tissues, which causes the bending of the rachises that characterizes the disease. Glyphosate applied to young palms caused anatomical changes similar to those observed in palms affected by crown disease.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
* Estacion Experimentala Fabio Baudrit, Costa Rica.
+ Laboratorio de Histologia, CATIE, Costa Rica.
** ASD de Costa Rica.