Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 33 (4) December 2021, p. 607-616
EVALUATION OF MITOCHONDRIAL DNA ISOLATION METHODS FOR OIL PALM (Elaeis guineensis) LEAF
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2021.0009
Received: 17 November 2020 Accepted: 11 January 2021 Published Online: 16 March 2021
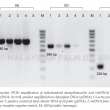
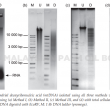
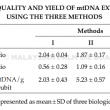
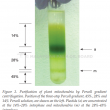
An efficient preparation of pure and intact mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA) that is free from nuclear DNA contamination is a prerequisite to study the molecular complexities of the organellar genome and gene structure in oil palm. Different extraction methods have been reported for mtDNA isolation from different plants. Using oil palm leaf tissues that are present in abundance, three methods were tested and modified to isolate mtDNA. The methods used vary primarily at the purification steps, either by using phenol/chloroform or density gradient centrifugation. High ionic alkaline buffer coupled with differential centrifugation were employed in Method I. While Methods II and III utilised the discontinuous sucrose and Percoll gradient centrifugation for mitochondria isolation, respectively. Method III provided good quality mtDNA from green leaves, yielding ~6.3 μg g–1 tissue. Restriction digest and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for regions specific to mitochondrial, nuclear and chloroplast DNA further verified the quality of the mtDNA from Method III, which had the least plastid DNA contamination. Method III that incorporated Percoll density gradient centrifugation was the most efficient and provided good quality mtDNA without nuclear DNA contamination for sequencing applications and studies requiring pure mtDNA.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
1 Malaysian Palm Oil Board,
6 Persiaran Institusi, Bandar Baru Bangi,
43000 Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia.
* Corresponding author e-mail: meilina@mpob.gov.my