Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 33 (1) March 2021, p. 140-150
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT FOR THE PRODUCTION OF PALM BIODIESEL
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2020.0080
Received: 18 March 2020 Accepted: 2 June 2020 Published Online: 7 October 2020
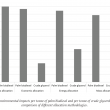
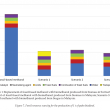
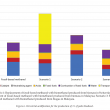
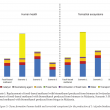
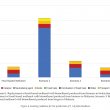
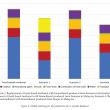
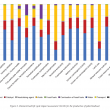
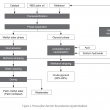
A gate-to-gate life cycle assessment (LCA) for the production of palm biodiesel was performed. The LCA study was conducted using SimaPro software version 8.5, and the impact assessment was performed according to ReCiPe 2016 methodology. A three-year (2015-2017) inventory data was obtained from five commercial palm biodiesel producers in Malaysia. Methanol, acids and sodium methoxide (catalyst) were identified as three major contributors to the environmental impacts. Impact assessment showed that replacement of fossilbased methanol with biomethanol produced from biogas is the most preferred option, saving up to 63% fossil resources and 22% reduction in global warming impact. Allocation based on economic value was found more suitable compared to mass or energy content. This is because both palm biodiesel and crude glycerol differ in terms of economic value and being used in different applications
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
* Malaysian Palm Oil Board,
6 Persiaran Institusi,
Bandar Baru Bangi,
43000 Kajang,
Selangor, Malaysia.
E-mail: clyung@mpob.gov.my
** Department of Civil Engineering,
Faculty of Engineering,
University of Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
‡ Institute of Ocean and Earth Sciences,
University of Malaya,
50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.