Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 33 (1) March 2021, p. 151-170
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF PALM OIL CLINKER AS A BINDER AND AGGREGATE REPLACEMENT IN CONCRETE
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2020.0081
Received: 14 February 2020 Accepted: 7 June 2020 Published Online: 7 October 2020
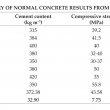
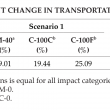
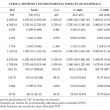
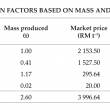
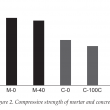
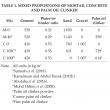
Palm oil clinker (POC) is a by-product derived from crude palm oil (CPO) production. Many studies have examined POC in concrete and it has often been stated as being environmentally sustainable. However, evidence to support these claims are not abundant in the literature. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the environmental impact of POC using a comparative, midpoints life cycle assessment approach based on 13 impact categories from ReCiPe2016. The use of POC as a binder replacement, fine aggregate and coarse aggregate was considered. Only production of cement, sand, gravel, POC and transportation were included in the system boundary. The construction, service and end-of-life phases were excluded. A volume of 1 m3 mortar or concrete with similar compressive strength was used as the functional unit. Life cycle inventory data was obtained from the literature, Malaysia Life Cycle Inventory Database (MY-LCID) and Ecoinvent database. Economic and mass allocation factors were calculated for POC. Calculations indicated that the use of POC in mortar and concrete showed reductions in all impact categories when economically allocated. When mass allocated, POC contributed minimally to all impact categories except ‘Freshwater Eutrophication’ and ‘Human Toxicity’. Despite these drawbacks, results show that use of POC resulted in an overall improvement for the environmental sustainability.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
* Department of Civil Engineering,
University of Malaya,
50603 Jalan Universiti,
Kuala Lumpur Malaysia.
E-mail: zainah@um.edu.my