Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 6 No. 1 1994 June, p. 25-38
MODIFICATION OF HYDROGENATED CANOLA OIL/PALM STEARIN/CANOLA OIL BLENDS BY CONTINUOUS ENZYMATIC INTERESTERIFICATION
Received: 10 February 1993 Accepted: 4 June 1993
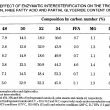
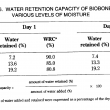
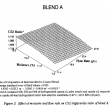
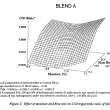
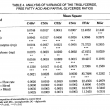
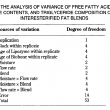
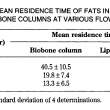
Three fat blends containing hydrogenated canola oil (HCO), palm stearic and canola oil (45/25/30%) were interesterified in a temperature and moisture controlled packed column reactor. The moisture of the fats was controlled by a pre-column packed with Biobone (a granulated chicken bone material possessing good mechanical strength). The changes in the composition of the major triglycerides (C48, C50, C52 and C54)were followed by GLC. Both the moisture content of the Bioboxe and the flow rate significantly affected the composition of C48, C52 and C54 triglycerides during interesterification. Other factors such as the age of the Lipozyme used, and that of the Biobone, also contributed to the variation in C48, C50 and C52 composition. An increase of more than 50% of C52 in the interesterified blends indicated that a large portion of the palmitic acid residues from the palm stearin were exchanged with an 18 carbon fatty acid present in the C54 molecules of the canola products. A flow rate of ll.4 g/h and a moisture content between 13.2% and 19.2% were most effective for interesterification.
However, the higher levels of free fatty acids (FFA), monoglycerides (MG) and diglycerides (DG) detected in the interesterified blends as compared with the control blends indicated that some degree of hydrolysis also occurred; the total amounts of FFA, MG and DG were higher by 5.9% to 13.O% in the interesterified blends.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
* Department of Food Science,
University of Guelph,
Ontario, Canada N1G 2W1.
** Department of Mathematics and Statistics / Department of Animal and Poultry Science,
University of Guelph,
Ontario, Canada N1G 2W1.