Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 33 (3) September 2021, p. 387-399
POTENTIAL OF FUNCTIONALISED CELLULOSE FROM OIL PALM BIOMASS AS NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS BASED NUTRIENT ADSORBENT – A REVIEW
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2020.0088
Received: 11 November 2019 Accepted: 8 July 2020 Published Online: 14 October 2020
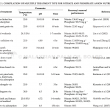
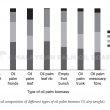
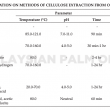
By the year 2020, oil palm biomass in Malaysia is projected to reach between 85-110 million tonnes per year. Instead of disposing off such a massive amount of biomass as waste, the oil palm biomass could be converted into value-added products. Since lignocellulosic materials could be a suitable adsorbent for nitrogen and phosphorus-based nutrients from aquaculture effluent based on studies conducted by other countries, it would be an excellent opportunity to monetise oil palm biomass for a similar purpose as well. There are many well-established extraction methods introduced by researchers. However, only a handful of the extraction method involved the use of green chemicals. This paper provides a review of the extraction and modification for oil palm biomass towards becoming a potential adsorbent for nitrogen and phosphorus-based nutrients.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
1 Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering,
Malaysia - Japan International Institute of Technology,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Jalan Sultan Yahya Petra,
54100 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2 Department of Environmental Engineering,
Faculty of Engineering and Green Technology,
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Jalan Universiti,
Bandar Barat, 31900 Kampar, Perak, Malaysia.
* Corresponding author e-mail: tan.liansee@utm.my