Journal of Oil Palm Research Vol. 5 No. 2 1993 Dec, p. 102-110
MICRONUTRIENTS IN PEAT: 1 PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS BY DIFFERENT EXTRACTION METHODS
Received: 11 December 1992 Accepted: 18 February 1993
Micronutrients especially Zn and Cu, are normally present in too low a concentration in peat to be adequately available to a crop.
This study was conducted to compare the characteristics of several classes of peat and to do a preliminary assessment on the actively and potentially plant-available form of micronutrients as a guide to the use in peat of fertilizers containing micronutrients.
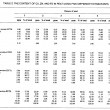
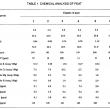
Five different extractants, namely ammonium acetate-EDTA, ‘double acids’ (0.05 N HCl/0.025 N H2SO4, 0.5 M HNO3, 0.1 M HCl and 0.2 N NaOH, were investigated on six different classes of peat.
The amounts of micronutrients extracted differed with the extractants used, depending on the nature of the peat, its drainage status and its agricultural utilization. Ammonium acetate-EDTA and NaOH were effective in extracting Cu and Fe: for example NaOH removed about 70%-93% of total Cu from peat. Ammonium acetate-EDTA, double acids, HCl and nitric acid were comparable, and appeared to be good extractants to displace Zn and Mn from peat. However, all the extractants studied merit further investigation to correlate the micronutrients extracted with the actual uptake by crops to obtain more useful and meaningful information on their availabilities in peat.
KEYWORDS:FIGURES & TABLES:
* Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia,
P O Box 10620,
50720 Kuala Lumpur